What Are the Differences Between Demand Planning and Supply Planning?
Demand planning and supply planning are two fundamental processes in any supply chain management system, ensuring the successful performance of a business. Although these terms are often used interchangeably, they refer to distinct functions that complement each other. Demand planning focuses on predicting what customers will need, or what future demand might be, while supply planning ensures that products and resources are available to meet that forecasted demand. Understanding the differences between these two processes is crucial for optimizing inventory management and improving the efficiency of a company’s supply chain optimization.
This article explores the core differences between demand planning and supply planning, their roles in supply chain management, and how they work together. Additionally, we will highlight the benefits of each process and explore why both are vital for businesses today.
What Is Demand Planning?
Demand planning refers to the process of forecasting customer demand for products or services over a specific period. It is one of the most essential corporate functions for businesses that aim to avoid costly issues such as overproduction or stockouts. Accurate customer demand forecasts allow companies to make more informed decisions about how much inventory they should maintain and when it should be replenished. Demand planning relies heavily on historical data, sales trends, and market research.
Key Components of Demand Planning:
- Demand Forecasting: This involves predicting future customer needs using various models and techniques. Historical sales data, seasonal patterns, and external factors like economic conditions or consumer behaviour are considered in this process.
- Time Series Analysis: Historical sales data plays a crucial role in demand planning. By understanding past sales patterns, businesses can prepare for periods of high demand or adjust inventory levels during slower seasons.
- Sales Trends and Market Research: Demand planners also consider changing consumer preferences, market trends, and competitive activity to ensure they stay ahead of shifting demand.
The main goal of demand planning is to ensure that businesses have the right products in stock to meet customer demand while avoiding overstocking. This reduces the risk of running out of products (stockouts) or holding excess inventory, which can lead to higher storage costs and waste.
What Is Supply Planning?
While demand planning predicts what customers will need in the future, supply planning ensures that businesses have the resources available to satisfy that demand. Supply planning involves the management of production schedules, procurement, and distribution of goods, and it works in conjunction with demand forecasts. Supply planners align production and operations with the forecasts developed by demand planners.
Key Components of Supply Planning:
- Production and Procurement Management: Supply planners collaborate with production teams to ensure manufacturing processes align with demand forecasts. They also liaise with suppliers to ensure that raw materials or finished products are available as needed.
- Aligning Supply with Demand Forecasts: Supply planning is based on the forecasts created by demand planners. For example, if a forecast predicts higher demand for a product, supply planners ensure that resources (such as materials, labour, and equipment) are available to meet that demand without delays.
- Resource Optimization: Supply planners focus on efficiently utilizing resources such as labour, raw materials, and production capacity to meet demand and minimize costs. This minimizes waste and improves overall supply chain efficiency.
Supply planning plays a critical role in product availability, cost minimization, and risk management within the supply chain, helping businesses reduce the disruptions associated with unforeseen demand shifts or supply chain interruptions.
Differences between Demand Planning and Supply Planning
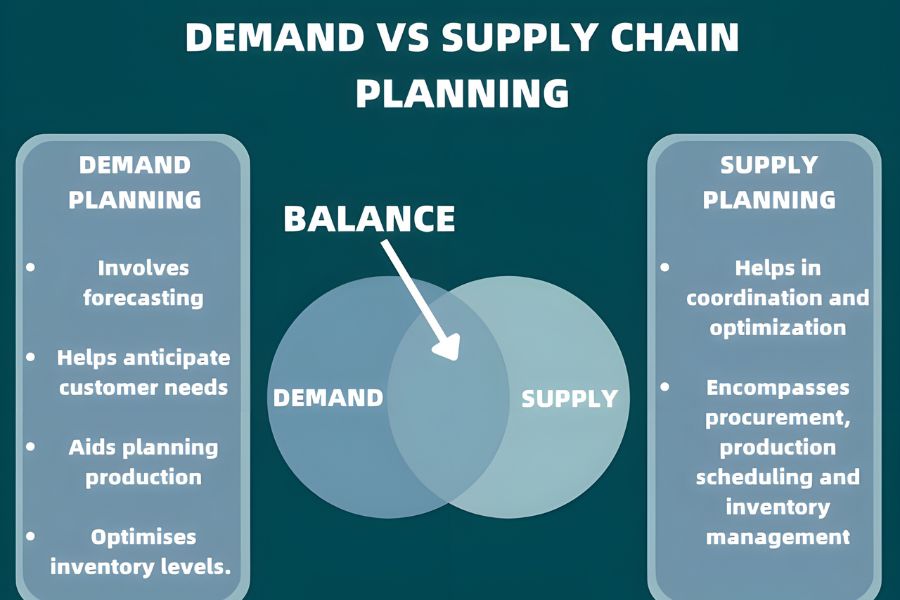
Although demand planning and supply planning are interconnected, they serve different purposes within the supply chain. Understanding these differences ensures that they can be combined effectively to optimize business performance.
Focus Areas:
- Demand Planning: Predicts future customer needs, helping businesses anticipate demand and plan accordingly.
- Supply Planning: Ensures that the company can meet forecasted demand through efficient production, procurement, and distribution processes.
Time Horizons:
- Demand Planning: Typically covers longer time horizons, ranging from months to years, to predict future sales and customer behavior.
- Supply Planning: Operates on much shorter time horizons, typically planning weeks or months in advance, to ensure that production and inventory can keep pace with demand.
Objectives:
- Demand Planning: Focuses on optimizing sales forecasts and maintaining stock levels that meet customer demand.
- Supply Planning: Focuses on producing and supplying products efficiently, minimizing costs while ensuring on-time delivery.
Methodologies and Tools:
- Demand Planning: Demand planners use statistical forecasting models, sales data analysis, and market research to predict future demand.
- Supply Planning: Supply planners use tools such as production scheduling software, inventory control systems, and procurement management systems to allocate resources effectively.
Benefit of Demand Planning

Effective demand forecasting offers several key benefits, which contribute to business success:
- Improved Forecast Accuracy: Accurate demand forecasts help businesses avoid the risks of overstocking or stockouts, resulting in more efficient inventory management.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: By anticipating customer demand, businesses can be well-prepared to meet it, leading to higher customer satisfaction and fewer missed sales opportunities.
- Cost Savings: Accurate forecasting helps avoid overproduction and excess inventory, reducing storage costs and minimizing waste.
- Effective Resource Utilization: Demand planning enables better purchasing decisions, production scheduling, and stock management, ensuring resources are used efficiently.
Benefits of Supply Planning
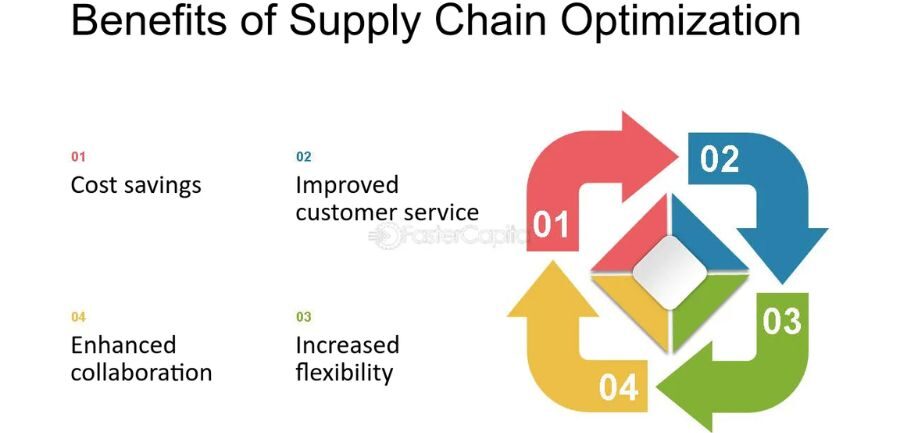
Supply planning also offers several unique benefits that contribute to operational efficiency:
- Minimizes Stockouts and Surplus: Supply planning reduces the risk of stockouts (which can lead to lost sales) and excess inventory (which ties up valuable resources) by aligning supply with demand.
- Cost Efficiency: Aligning production with demand forecasts helps businesses reduce waste, minimize labour costs, and lower material and storage expenses.
- Smooth Operations: Supply planning facilitates smooth operations with fewer disruptions and delays by synchronizing production schedules with demand.
- Risk Management: Supply planners can anticipate potential supply chain disruptions, such as raw material delays or unexpected demand spikes, and take steps to mitigate risks, ensuring business continuity.
How do Demand and Supply Planning Work Together?
While demand planning and supply planning differ in their objectives, they are deeply interconnected. Demand planning generates the forecasts that supply planning relies on to ensure production and distribution processes run smoothly.
For example, if demand planners predict a surge in demand for a particular product, supply planners must ensure that production and procurement are aligned to meet this demand. Failure to do so may result in stockouts, lost revenue, and customer dissatisfaction. Conversely, if demand is overestimated, it can lead to excessive inventory, wasted resources, and higher operational costs.
When demand and supply planning are properly integrated, businesses can maintain optimal inventory levels, reduce waste, and improve overall supply chain performance.
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
What is demand planning?
Demand planning is the process of forecasting future customer demand for products or services based on historical data, sales trends, and market research.
What is supply planning?
Supply planning ensures that the resources, products, and materials are available to meet the forecasted customer demand through efficient production, procurement, and distribution.
How are demand planning and supply planning different?
Demand planning focuses on predicting future customer needs, while supply planning ensures that the company has the resources to meet these needs through production and inventory management.
How do demand planning and supply planning work together?
Demand planning forecasts customer needs, while supply planning aligns production and resource allocation to meet those forecasts. Effective collaboration between the two ensures smooth supply chain operations.
End Notes
At KnoWerX, we know that both demand planning and supply planning are important parts of managing the supply chain well. They each play a different but balanced role. People can learn how to do these things with our help through courses like CFDM (Certified Forecasting and Demand Management) and the APICS Supply Chain Planning Certificate. Demand planning is the process of correctly predicting what customers will want in the future, and supply planning is the process of making sure that there are enough resources to meet those needs.
By aligning demand and supply planning processes, companies can minimize stockouts, reduce excess inventory, and create a more efficient and resilient supply chain management system, driving greater profitability and long-term success.
Image Reference: Freepik
Disclaimer: All trademarks, logos, and brand names are the property of their respective owners. All company, product, and service names used in this website are for identification purposes only. Use of these names, trademarks, and brands does not imply endorsement.



