Benefits of SCM Online Course for New-Age Pros

Benefits of SCM Online Course for New-Age Pros In today’s fast-evolving business ecosystem, supply chains have emerged as the lifelines of global trade. From sourcing raw materials to delivering final products to customers, every step requires careful coordination. With increasing digitalisation and global competition, supply chain professionals must stay ahead of the curve. One effective way to do that is by upskilling through online training. The Benifits of SCM online course for modern professionals are vast from career growth and global recognition to digital agility and leadership readiness. Whether you’re an aspiring executive or an experienced manager seeking to upgrade your skills, SCM e-learning programmes can help you unlock your potential and seize new opportunities. Why Choose an Online SCM Course? Flexibility & Convenience One of the most compelling reasons to choose an online SCM course is the flexibility it offers. Unlike traditional classroom programmes that require strict attendance and fixed schedules, online courses allow you to learn at your own pace ideal for professionals managing jobs, families, or multiple commitments. For learners who may be located far from urban training centres, virtual classrooms are also more accessible. You can log in from anywhere and still benefit from global-standard education without relocating. Cost-Effective & Time-Saving Besides flexibility, online courses tend to be more cost-effective than in-person alternatives. You save not only on travel and accommodation but also on tuition fees. Many programmes offer value-added resources such as downloadable content, live instructor sessions, and community discussion forums. Moreover, online SCM certifications focus on real-world applications, enabling professionals to apply concepts immediately in their work environments. This quick integration of knowledge into practice is another critical factor behind the Benifits of SCM online course. Up-to-Date, Industry-Aligned Curriculum Today’s supply chain challenges such as global disruptions, inflation, and digital transformation—require cutting-edge knowledge and tools. Reputable online SCM platforms like KnoWerX keep their curriculum updated with the latest industry frameworks, analytics tools, and case studies. From SCOR models to risk management strategies, you gain exposure to real-world business scenarios. These practical insights elevate your understanding far beyond textbook theory. Skills You Gain from SCM Online Courses Strategic Sourcing & Procurement Strategic sourcing is a vital component of supply chain success. An SCM course introduces you to techniques like supplier segmentation, cost modelling, and vendor contract negotiation. These skills are invaluable when working in procurement, operations, or supply chain planning roles. Inventory Management & Demand Forecasting One of the most tangible Benifits of SCM online course programmes is the knowledge of inventory control techniques. You’ll learn how to optimise inventory levels using ABC classification, EOQ models, and safety stock calculations ensuring service levels while minimising excess stock. Demand forecasting modules teach you how to use historical data, market insights, and statistical tools to predict future needs, improving customer satisfaction and profitability. Logistics, Distribution & Transportation Online SCM courses provide in-depth exposure to logistics functions such as warehousing, transport optimisation, multimodal shipping, and last-mile delivery. You’ll gain insights into how global supply chains operate across regions, how customs and documentation impact flow, and how technology enables real-time tracking. ERP & Supply Chain Software Tools Digital fluency is now a must-have skill in supply chain roles. Through platforms like KnoWerX’s Certifications & Training, you get introduced to ERP systems such as SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft Dynamics. Some courses also integrate supply chain simulation games and modelling tools to give you hands-on experience in real-world scenarios. Analytics, KPIs & Decision-Making Modern SCM roles demand strong analytical capabilities. Online courses help you understand performance metrics like fill rate, OTIF (on-time-in-full), inventory turnover, and working capital. These indicators are vital in making strategic supply chain decisions. Impact of SCM Training on Your Career Job Market Competitiveness Certifications from respected institutes give you a significant edge during recruitment. Recruiters actively seek candidates who possess globally recognised credentials like CSCP, CPIM, or CLTD available through KnoWerX, India’s Premier Elite APICS partner. Whether you’re aiming for a promotion, switching industries, or stepping into leadership roles, SCM training signals your readiness to take on responsibility. Higher Salary Potential Studies consistently show that professionals with supply chain certifications earn more than their uncertified peers. By developing skills that directly impact business performance like demand planning, cost reduction, and risk management—you can justify higher pay and added value in the organisation. Global Career Versatility From FMCG to automotive, healthcare to e-commerce supply chain is central to nearly every industry. With the Benifits of SCM online course, you gain a skillset that is transferable across domains and geographies. This broad applicability makes SCM an attractive career path for global-minded professionals. Confidence through Real Case Studies Case-based learning forms the heart of many SCM courses. You’ll analyse complex supply scenarios and devise actionable strategies. These exercises not only sharpen your decision-making but also prepare you to lead during real crises like raw material shortages or freight disruptions. For ongoing industry insights, KnoWerX also shares valuable thought leadership through its Supply Chain Blog. Benifits of SCM Online Course for New-Age Professionals Adapt to a Digitally Disruptive World With AI, IoT, blockchain, and big data transforming supply chains, staying updated is not optional—it’s essential. Online courses help you master modern digital tools and concepts like DDMRP (Demand Driven MRP), predictive analytics, and SCOR modelling, making you future-ready. Bridge the Theory-Practice Gap University education often lacks exposure to practical business challenges. The Benifits of SCM online course include applied learning through simulations, real-time assignments, and expert webinars, helping you transition from academic knowledge to actionable expertise. Join a Global Learning Community Online SCM courses connect learners from around the world. This interaction with professionals from diverse sectors creates a robust network of peers, mentors, and future collaborators. Receive Industry-Recognised Certification When you choose an accredited provider like KnoWerX, you earn internationally respected credentials from APICS, DDI, and SCOR. These qualifications open doors not just in India, but across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. Why Choose KnoWerX for SCM Training? 30+ Years of Expertise in SCM Training Established in 1992, KnoWerX
Get CLTD Online Certification – Your Logistics Career Awaits
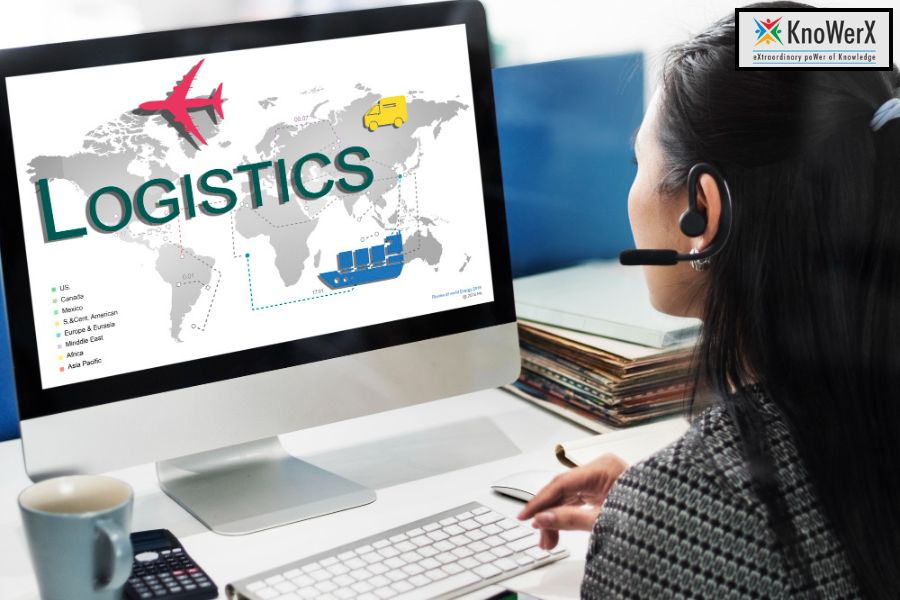

Get CLTD Online Certification– Your Logistics Career Awaits! The global logistics industry is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by innovations in technology, the rise of e-commerce, and the increasing need for seamless transportation and distribution networks. To stay ahead of the curve, professionals must be equipped with advanced skills and recognised credentials. One such credential that stands out is the CLTD (Certified in Logistics, Transportation and Distribution) certification. Opting for a CLTD online certification gives you the flexibility to master logistics fundamentals and specialised knowledge without disrupting your professional commitments. Whether you aim to lead strategic supply chain operations or enhance your current role, this certification opens doors to endless opportunities in a competitive global market. What Is CLTD? CLTD, which stands for Certified in Logistics, Transportation and Distribution, is a globally recognised certification offered by APICS, a part of the Association for Supply Chain Management (ASCM). It validates your expertise in a wide range of logistics topics, including: Logistics strategy and planning Transportation and distribution management Warehouse operations Inventory and order management Global logistics considerations The CLTD certification is ideal for logistics managers, distribution professionals, supply chain analysts, and anyone aspiring to specialise in logistics. Why Choose a CLTD Online Certification? Flexibility and Convenience One of the biggest advantages of CLTD online certification is its flexibility. You can learn at your own pace, making it perfect for working professionals or students balancing other responsibilities. Access to Digital Resources Online certification programs provide a wealth of digital tools, including interactive study guides, video lessons, eBooks, and online discussion forums. This ensures a comprehensive and engaging learning experience. Remote Exam Options With an online CLTD program, even the exam can be taken remotely. Proctored online tests allow candidates to take the certification exam from the comfort of their home or office. Cost-Effective Learning Online programs often come at a lower cost than in-person training. They also reduce travel expenses, accommodation costs, and time off work, making CLTD online certification a budget-friendly option. Learning Without Geographic Boundaries Since CLTD online certification is accessible from anywhere, it allows individuals from remote or international locations to benefit from top-tier logistics education. Course Structure and Learning Modules The CLTD online certification course is structured into eight main modules: Logistics Overview & Strategy Capacity Planning & Demand Management Order Management Inventory & Warehouse Management Transportation Management Global Logistics Logistics Network Design Reverse Logistics & Sustainability Each module is designed to provide in-depth knowledge and practical insights that professionals can apply directly to their roles. Learners can access case studies, scenario-based questions, and real-world examples to reinforce concepts and apply them in their organisations. Career Opportunities After CLTD Certification Pursuing a CLTD online certification significantly enhances your career prospects. Here are some of the job roles you can pursue: Logistics Manager Distribution Centre Supervisor Supply Chain Analyst Inventory Control Specialist Transportation Manager With global logistics becoming increasingly complex, certified professionals are in high demand across various industries, including retail, manufacturing, healthcare, and e-commerce. Higher Salary Potential CLTD-certified professionals often command higher salaries due to their specialised knowledge and credibility in logistics. Global Recognition The certification is recognised internationally, opening doors to global career opportunities and cross-border job roles. Opportunity to Lead Professionals with a CLTD online certification are more likely to be entrusted with leadership roles and strategic responsibilities in logistics operations. Key Benefits of CLTD Online Certification Enhances Professional Credibility Being CLTD-certified showcases your commitment to professional development and your competence in handling complex logistics functions. Helps in Decision-Making The certification equips you with tools and strategies that improve decision-making, reduce costs, and increase supply chain efficiency. Keeps You Updated The dynamic logistics environment demands continuous learning. A CLTD online certification helps you stay updated with global trends and best practices. Improves Operational Efficiency Certified professionals often introduce efficient processes in transportation, warehousing, and inventory management, contributing to an organisation’s bottom line. Builds Confidence and Problem-Solving Skills Through structured learning and practical assessments, CLTD online certification enhances your ability to solve real-world logistics challenges. Tips to Succeed in CLTD Online Preparation Set a Study Schedule: Allocate time daily or weekly for your studies and stick to it. Use Official Resources: Invest in official CLTD Learning Systems and exam simulators. Join Online Forums: Participate in CLTD study groups or forums for peer support. Take Practice Tests: These simulate the real exam environment and boost confidence. Engage with Instructors: When available, make the most of instructor-led sessions to clarify doubts. Review Regularly: Frequent revision of topics ensures better retention and understanding. Why Choose KnoWerX for Your CLTD Journey? KnoWerX is a leading provider of Supply Chain Management and logistics training in India. Here’s why it’s the ideal partner for your CLTD online certification journey: Expert Faculty: Industry professionals with real-world experience Flexible Learning Options: Self-paced and instructor-led online programs Official APICS Learning Partner: Ensures access to authentic and updated material Support & Mentorship: Continuous guidance through your learning journey Proven Success: High pass rates and excellent student feedback Career Guidance: KnoWerX offers support even after certification to help professionals make the most of their qualifications Frequently Asked Questions Ending Notes The logistics industry is evolving, and the demand for certified professionals is at an all-time high. Getting your CLTD online certification not only boosts your knowledge but also positions you as a competent, future-ready professional. Whether you’re just starting or looking to climb higher in your logistics career, now is the time to act. With KnoWerX, you gain more than just training; you gain a trusted partner in your professional journey. Start your CLTD online certification today and unlock a world of opportunities. Your logistics career awaits! Image Reference: Freepik Disclaimer: All trademarks, logos, and brand names are the property of their respective owners. All company, product, and service names used in this website are for identification purposes only. Use of these names, trademarks, and brands does not imply endorsement.
Unlock Career Growth: Top Benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0

Unlock Career Growth: Top Benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0! In today’s fast-paced, globalised world, managing supply chains efficiently is more critical than ever. The APICS Certified in Planning and Inventory Management (CPIM) 8.0 is one of the most respected certifications for supply chain professionals. With a refreshed structure and updated content, CPIM 8.0 is tailored to match the evolving demands of modern industry. In this article, we explore the benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0, covering how it impacts professional development, enhances learning, and boosts business outcomes. Understanding the APICS CPIM 8.0 Certification What Is CPIM 8.0? APICS, now part of the Association for Supply Chain Management (ASCM), developed CPIM (Certified in Planning and Inventory Management) to validate an individual’s expertise in operations and supply chain. The 8.0 version is the latest iteration, combining decades of industry insights with current trends and technologies. This version simplifies the previous two-part exam into a single, unified format and focuses more on real-world applications, strategic thinking, and digital competencies. The benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0 extend far beyond passing an exam—they enhance career readiness, decision-making skills, and operational efficiency. Enhanced Curriculum and Updated Content Aligned with Global Supply Chain Practices One of the standout benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0 is its alignment with today’s global supply chain standards. Unlike earlier versions, CPIM 8.0 incorporates frameworks used by top multinational companies and integrates concepts such as: Integrated business planning Enterprise resource planning (ERP) Sales and operations planning (S&OP) Digital supply chain transformation This ensures that professionals are learning the most up-to-date methodologies and strategies used in the real world. Relevance to Current Business Challenges CPIM 8.0 addresses pressing challenges faced by supply chains globally, such as disruptions, inflation, inventory volatility, and digital automation. This modern focus equips professionals with the tools to respond effectively to rapid changes, making the benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0 crucial in a VUCA (Volatile, Uncertain, Complex, and Ambiguous) environment. Improved Learning Experience Streamlined Structure for Better Focus One of the most user-friendly benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0 is its revamped structure. Instead of two separate modules, CPIM 8.0 features a single, cohesive learning path. This streamlined approach helps learners maintain focus and momentum, reducing the time and effort required to prepare. Flexibility with Online Learning Tools CPIM 8.0 offers blended learning experiences with online courses, mobile-friendly content, self-paced modules, and virtual simulations. These tools allow working professionals to prepare without disrupting their schedules. With these features, the benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0 make certification more accessible to a wider range of learners, from recent graduates to senior managers. Practice Tests and Assessments Interactive assessments and mock exams allow learners to gauge their understanding and identify areas that need improvement. These features enhance retention and confidence, making the benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0 evident throughout the learning process. Career Advancement Opportunities Recognition Across Industries The CPIM 8.0 certification is globally recognised and respected across industries including manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, automotive, and retail. Having this credential on your resume increases credibility and positions professionals as supply chain experts. One of the primary benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0 is that it signals to employers that you possess advanced planning and inventory management capabilities. Path to Promotions and Pay Raises Professionals with CPIM certification are more likely to receive promotions, take on leadership roles, and command higher salaries. Studies have shown that certified individuals earn up to 27% more than their non-certified peers. These tangible outcomes are among the most rewarding benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0 for career growth. Strategic Decision-Making Skills CPIM 8.0 fosters critical thinking and problem-solving, especially in supply chain design, capacity planning, and inventory control. Professionals gain the ability to make data-driven decisions that positively impact their organisation’s bottom line. This strategic mindset is one of the transformative benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0. Organisational Benefits Increased Operational Efficiency Employers who encourage their teams to pursue CPIM certification report significant improvements in productivity and efficiency. CPIM 8.0 provides knowledge that helps streamline workflows, optimise inventory levels, and reduce waste. These are measurable benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0 at the organisational level. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication Certified professionals understand the language of supply chain across departments, which improves cross-functional communication. From procurement to production and sales, CPIM 8.0 helps integrate the entire supply chain ecosystem. This harmonisation is among the most practical benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0 for businesses. Risk Mitigation and Business Resilience With modules focused on risk management, contingency planning, and supply chain continuity, CPIM 8.0 prepares individuals to manage uncertainties. Organisations with CPIM-certified professionals are better equipped to handle disruptions, making this one of the most strategic benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0. Validation of Professional Expertise Internationally Recognised Credential The CPIM 8.0 is not just another certification it’s a mark of excellence. Whether you’re in India, the USA, the Middle East, or Europe, the credential speaks the universal language of supply chain proficiency. This broad recognition is among the key benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0 for those looking to work globally. Demonstrates Commitment to Professional Growth Earning the CPIM 8.0 certification showcases a proactive attitude toward learning and professional development. It demonstrates that a candidate is committed to mastering the intricacies of supply chain management. This perception among employers is one of the subtle yet powerful benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0. Builds Confidence and Credibility CPIM-certified professionals often take on mentoring roles within their organisations. Their certification gives them the confidence to guide others, take initiative, and lead projects. This development of leadership capabilities further adds to the benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0. Competitive Advantage in the Job Market Preferred by Recruiters With the rise of supply chain digitisation, companies are looking for certified professionals who understand integrated systems. Recruiters often prefer candidates with CPIM credentials, making job applications more competitive. One of the leading benefits of APICS CPIM 8.0 is that it boosts visibility and appeal in the job market. Cross-Functional Role Opportunities Beyond traditional supply chain roles, CPIM 8.0 opens doors to careers in procurement, demand
Understanding 4 Components of Inventory Management

Understanding 4 Components of Inventory Management At KnoWerX, we believe that mastering the fundamentals is key to unlocking long-term success in the world of supply chain and operations. With over 33 years of collective experience, our mission is to simplify complex processes and help professionals across industries become experts through our industry-leading training programs. One of the most essential areas in the supply chain process is It is the backbone of supply continuity and operational efficiency. In this article, we’ll break down the 4 core components of inventory management and share practical tips to understand and manage them effectively. 1. Inventory Control – The Foundation of Inventory Management Inventory control focuses on the regulation and supervision of stock to maintain the right balance – not too much and never too little. ✅ Tips for Effective Inventory Control: Establish Minimum and Maximum Stock Levels: Set threshold levels for each product to avoid overstocking and stockouts. Use ABC Analysis: Categorise inventory into three groups (A – high value, B – moderate value, C – low value) to prioritise control efforts. Implement FIFO or LIFO Methods: Use First-In-First-Out or Last-In-First-Out strategies depending on the nature of your inventory. Leverage Inventory Management Software: Invest in tools that automate stock monitoring, generate alerts, and provide real-time data. At KnoWerX, our inventory management training emphasises the importance of building a solid inventory control process that can be scaled as business needs grow. 2. Inventory Forecasting – Anticipate Demand Accurately Forecasting is the predictive component of inventory management, helping organisations estimate future demand and align inventory levels accordingly. ✅ Tips for Inventory Forecasting: Analyse Historical Sales Data: Review past data to identify seasonal patterns, sales cycles, and customer preferences. Collaborate Across Departments: Sales, marketing, and finance teams should all contribute to accurate demand forecasts. Factor in External Influences: Account for holidays, market trends, economic shifts, and promotional campaigns. Use Forecasting Software: Tools integrated with your inventory management system can improve accuracy through AI and machine learning. Professionals trained at KnoWerX learn to build data-driven forecasting models that ensure optimised inventory levels and reduce excess carrying costs. 3. Inventory Procurement – The Art of Timely Replenishment Procurement is about sourcing the right quantity of inventory at the right time and cost. It is a strategic component that directly impacts cost efficiency. ✅ Tips for Smart Inventory Procurement: Choose Reliable Suppliers: Build relationships with vendors who are consistent in quality and delivery timelines. Utilise Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): Calculate the most cost-effective quantity to order, balancing holding and ordering costs. Adopt Just-In-Time (JIT) Strategies: Reduce carrying costs by ordering inventory only when needed. Monitor Supplier Performance: Regular evaluations help ensure that procurement practices support efficient inventory management. With KnoWerX’s specialised training, professionals gain real-world insights into supplier selection, order timing, and cost negotiation to enhance procurement practices. 4. Inventory Auditing – Ensuring Accuracy and Accountability Auditing is the verification process in inventory management that ensures what’s recorded matches physical inventory. ✅ Tips for Thorough Inventory Auditing: Conduct Cycle Counting: Regularly count subsets of inventory to avoid year-end bottlenecks. Use Barcoding and RFID: Automate data entry and reduce human errors through technology. Implement Audit Trails: Maintain a digital trail of every movement and adjustment made in the inventory. Train Staff on Best Practices: Everyone handling inventory should understand the importance of accurate data. Our programs at KnoWerX prepare professionals to implement foolproof auditing systems that prevent loss, theft, and mismanagement. The Role of Technology in Inventory Management Digital transformation has reshaped inventory management. Technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain are enabling real-time visibility, automation, and predictive analytics. ✅ Tips for Embracing Technology: Invest in Cloud-Based Inventory Solutions: Access data anytime, anywhere. Implement IoT Sensors: Gain real-time insights into stock movement and warehouse conditions. Use AI for Predictive Analytics: Forecast demand more accurately with machine learning algorithms. Integrate Systems: Ensure your inventory tools communicate with procurement, sales, and finance platforms. Inventory Management Metrics to Track To gauge the effectiveness of your inventory management strategy, monitor these essential metrics: Inventory Turnover Ratio: How often inventory is sold and replaced. Carrying Cost of Inventory: Total cost to hold inventory over a period. Order Accuracy Rate: Percentage of orders fulfilled without errors. Stockout Rate: How frequently items go out of stock. Tracking these KPIs helps in making informed decisions and highlights areas needing improvement Sustainable Inventory Management Practices As environmental concerns grow, sustainability is becoming integral to inventory management. ✅ Tips for Greener Inventory Practices: Minimise Overstocking: Reduce waste and obsolete inventory. Optimise Transportation Routes: Cut emissions with better logistics planning. Source Locally: Reduce carbon footprint and support local economies. Recycle and Reuse Packaging: Lower costs and promote eco-conscious branding. The KnoWerX Advantage in Inventory Management Training Understanding and mastering these 4 components of inventory management – control, forecasting, procurement, and auditing – is critical for any supply chain professional. At KnoWerX, we go beyond just teaching the concepts. Our programs include hands-on simulations, real-life case studies, and mentoring from industry veterans. 📌 Why Choose KnoWerX? 33+ years of expertise in education and consultancy. Global exposure, having trained professionals from large companies in India and abroad. Best-in-class pricing for the highest quality education. One-stop destination for certifications, domain knowledge, and career advancement in supply chain. Frequently Asked Questions Final Thoughts Effective inventory management is not just about keeping track of goods. It’s a dynamic discipline that requires strategic planning, technological integration, and continuous improvement. By understanding the 4 components of inventory management, professionals can contribute significantly to cost savings, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction. If you’re looking to enhance your career in supply chain, consider enrolling in our professional training courses at KnoWerX. Learn from the best, and become the expert your organisation needs. Visit us today to explore our offerings and take the first step toward inventory mastery! Image Reference: Freepik Disclaimer: All trademarks, logos, and brand names are the property of their respective owners. All company, product, and service names used in this website are for identification purposes only. Use of
Why Supply Chain Transformation is a Must Now

Why Supply Chain Transformation is a Must Now – The Complete Guide Supply chain transformation refers to the comprehensive rethinking and restructuring of supply chain processes, systems, and strategies to better align with the changing demands of the global market. Unlike incremental improvements, transformation entails adopting innovative technologies, reengineering workflows, and reshaping supply chain models to drive long-term resilience and performance. Since 2020, businesses have faced significant disruptions that exposed the vulnerabilities of traditional supply chain models. From the COVID-19 pandemic to geopolitical tensions and inflationary pressures, these global shocks have underscored the urgent need for businesses to future-proof their supply chains. In this complete guide, we explore the key reasons driving the transformation, core components of a modern supply chain, step-by-step processes to begin your transformation journey, the challenges involved, real-life case studies, and future trends that will redefine supply chain success. The Need for Urgency: What’s Changed in Supply Chains Impact of Global Disruptions: The COVID-19 pandemic brought supply chains to a standstill, causing delays, stockouts, and cost escalations. The Russia-Ukraine war and trade tensions have further strained global networks. These events have demonstrated that supply chains can no longer be reactive; they must be proactive, responsive, and resilient. Rising Customer Expectations: Today’s consumers expect real-time visibility, faster delivery, and seamless omni-channel experiences. Supply chains must adapt to meet these expectations, ensuring flexibility and transparency across the entire delivery journey. Regulatory and Sustainability Demands: Governments and regulatory bodies are enforcing stricter environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards. From carbon emissions reporting to ethical sourcing requirements, organisations must transform their supply chains to comply with new regulations. Digital Disruption: The acceleration of technology is reshaping how supply chains operate. Companies must embrace digital tools to remain competitive, from cloud computing and big data to machine learning and robotic process automation (RPA). Key Drivers of Supply Chain Transformation Demand Volatility and Inventory Visibility: Consumer demand patterns have become unpredictable. Accurate forecasting and inventory visibility are vital for managing stock levels, minimising waste, and ensuring timely fulfilment. ESG and Sustainability Goals: Organisations are now being held accountable for their environmental impact. Green logistics, waste reduction, and circular supply chain models are no longer optional – they are imperative. Shift from Globalisation to Regionalisation: Companies are reducing dependence on global suppliers and moving toward regionalised networks to improve supply continuity and reduce risks from geopolitical issues. Data and Analytics as a Differentiator: Harnessing data enables businesses to identify inefficiencies, predict disruptions, and make data-driven decisions. Predictive analytics and real-time insights offer a significant competitive edge. Labour Shortages and Skills Gap: The shortage of skilled labour is a growing concern. Businesses must invest in upskilling employees and automating repetitive tasks to maintain operational efficiency. Core Pillars of a Transformed Supply Chain Digitalisation & Automation AI, IoT, Blockchain, and Robotics: Artificial Intelligence (AI) is used for forecasting, automation, and anomaly detection. Internet of Things (IoT) devices enable real-time tracking of goods. Blockchain ensures transparent and tamper-proof record-keeping, while robotics streamline warehouse operations and last-mile delivery. Resilience & Agility Scenario Planning, Dual Sourcing, Buffer Stock: Building resilience involves planning for multiple scenarios, diversifying suppliers, and maintaining safety stock. Agility ensures businesses can quickly pivot in response to changes in demand or disruptions. Customer-Centric Supply Chain Last-Mile Delivery, Personalisation, Omni-Channel Fulfilment: A modern supply chain is designed around the customer. This includes enabling faster last-mile delivery, offering personalised products and services, and integrating online and offline fulfilment channels. Data-Driven Decision Making Advanced Analytics, Real-Time Dashboards: Real-time data visualisation dashboards and predictive analytics help companies anticipate issues, optimise routes, manage inventory, and improve performance across the board. Sustainability Integration Green Logistics, Circular Economy, Carbon Reduction: Sustainability is embedded into every layer of a modern supply chain. Companies are adopting electric delivery vehicles, recycling packaging materials, and aiming for net-zero emissions. Steps to Begin Supply Chain Transformation Assessment & Benchmarking: Begin with a detailed assessment of your existing supply chain. Benchmark performance against industry standards to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement. Define Vision and Strategic Objectives: Establish a clear vision for transformation. Align objectives with broader business goals, including efficiency, customer satisfaction, risk mitigation, and sustainability. Invest in the Right Technology: Choose technologies that align with your strategy. Cloud platforms, ERP systems, AI tools, and automation technologies should be scalable and compatible with your existing infrastructure. Change Management & Talent Upskilling: Transformation is as much about people as it is about technology. Implement change management strategies and train your workforce to adopt new tools and workflows. Pilot Programs and Phased Implementation: Test new solutions through pilot projects. Use lessons learned to refine your approach and scale in phases to minimise disruption and maximise ROI. Challenges to Expect – And How to Overcome Them Resistance to Change: Employees may resist new technologies or fear job displacement. Clear communication, involvement in planning, and training can ease transitions. Integration Issues: Legacy systems can hinder integration. A strong IT strategy, middleware solutions, and API-driven architecture can enable seamless connectivity. Budget Constraints: Transformation requires investment. Prioritise initiatives with quick wins and high ROI to secure buy-in and justify further funding. Data Quality and Cybersecurity: Poor data quality leads to poor decisions. Implement data governance policies and cybersecurity protocols to safeguard operations. Stakeholder Alignment: Ensuring alignment across departments can be challenging. Regular updates, workshops, and cross-functional teams foster collaboration and alignment. Case Studies: Success Stories in Supply Chain Transformation Example 1: Walmart Walmart implemented predictive analytics and IoT technologies to enhance inventory management and customer experience. Their investments have resulted in increased stock availability and reduced waste. Example 2: Unilever Unilever embraced a sustainable supply chain by reducing emissions and increasing supply chain transparency. They leveraged blockchain to track materials from source to shelf. Example 3: DHL DHL integrated robotics and AI in their warehouses to optimise logistics and improve delivery speed. Their innovation hubs promote continuous improvement and tech adoption. The Role of Leadership in Driving Change CEO and CSCO Alignment: Leadership must be united in their commitment to transformation. The
How to Dominate Logistics and Distribution in 2025

How to Dominate Logistics and Distribution in 2025 The landscape of Logistics and Distribution is rapidly evolving. With technological advancements, changing consumer expectations, and global uncertainties, businesses in 2025 need to be more agile, efficient, and intelligent than ever before. To succeed, professionals must focus on a strategic mix of innovation, workforce development, and customer-centric operations. In this article, we explore the key pillars to help you dominate Logistics and Distribution in 2025. Embrace Tech-Driven Transformation Leverage Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning have become essential tools in the realm of Logistics and Distribution. These technologies enable businesses to make smarter decisions by analysing large volumes of data. Predictive analytics, powered by machine learning, can forecast demand more accurately, reduce errors, and improve inventory planning. In transportation, AI algorithms can optimise delivery routes, saving time and reducing fuel costs. Implement Internet of Things for Real-Time Visibility The Internet of Things connects physical devices, allowing for seamless communication and data exchange across the supply chain. In Logistics and Distribution, IoT enables real-time tracking of shipments, improving transparency and customer satisfaction. It also facilitates condition monitoring for temperature-sensitive goods, ensuring compliance with safety and quality standards. Companies that invest in IoT infrastructure are better positioned to react swiftly to disruptions and delays. Adopt Blockchain for Security and Transparency Blockchain technology introduces a secure, tamper-proof method of recording transactions and tracking assets. In Logistics and Distribution, blockchain ensures authenticity and accountability across the entire supply chain. It allows all parties to view a single version of the truth, which is crucial for traceability and fraud prevention. By adopting blockchain, companies can foster trust and collaboration with partners and clients. Optimise Warehouse and Fulfilment Operations Invest in Robotics and Automation Automation is transforming warehouse operations across the globe. The use of robotics for picking, packing, and sorting reduces manual labour and human error. Automated systems can operate round-the-clock, increasing throughput and reducing operational costs. In Logistics and Distribution, automation enhances efficiency, improves accuracy, and accelerates order fulfilment. Develop Flexible Warehouse Networks The traditional model of large central warehouses is being replaced by decentralised networks. Micro-fulfilment centres located closer to urban populations enable faster delivery and reduced transportation costs. These flexible networks are especially beneficial for e-commerce businesses. They allow companies to respond quickly to demand fluctuations and minimise last-mile delivery challenges. Use Data-Driven Inventory Management Data analytics is a critical component of modern inventory management. Companies that utilise real-time data can make informed decisions about stock levels, replenishment timing, and product placement. Just-In-Time restocking minimises excess inventory, lowers storage costs, and prevents stockouts. Cloud-based inventory systems provide visibility and control across multiple locations, improving overall operational efficiency in Logistics and Distribution. Build a Resilient and Agile Distribution Network Diversify Carrier and Supplier Relationships Relying on a single supplier or logistics provider can be risky. Diversifying your network of carriers and suppliers ensures continuity in case of disruption. Building relationships with regional and local partners allows for quicker response times and better adaptability. This diversity enhances the robustness of your Logistics and Distribution system. Prepare Effective Contingency Plans Unforeseen events such as natural disasters, pandemics, or political unrest can disrupt supply chains. Having contingency plans in place enables businesses to react quickly and maintain operations. These plans may include rerouting options, emergency inventory reserves, or alternative suppliers. In Logistics and Distribution, preparedness is a competitive advantage. Implement Dynamic Route Planning Advanced route planning tools use data such as weather, traffic conditions, and vehicle availability to determine the most efficient delivery paths. Integrating these tools with GPS and Transport Management Systems ensures timely deliveries and optimal fuel usage. Businesses that use dynamic route planning can reduce delivery times and increase customer satisfaction. Prioritise Customer-Centric Logistics and Distribution Offer Same-Day and Next-Day Delivery Options Today’s consumers demand speed and convenience. Providing same-day or next-day delivery options can set your business apart from competitors. To meet these expectations, companies must invest in local fulfilment centres and efficient delivery networks. Fast delivery enhances customer loyalty and boosts brand reputation in the Logistics and Distribution sector. Provide Transparent Tracking and Communication Customers want to know the status of their orders in real time. Offering tracking features and proactive communication builds trust and reduces customer inquiries. User-friendly dashboards and automated notifications keep customers informed throughout the delivery process. Transparency in Logistics and Distribution strengthens the customer experience. Integrate Sustainable and Ethical Practices Sustainability is no longer optional. Businesses that prioritise environmental responsibility gain favour with customers and stakeholders. Initiatives such as eco-friendly packaging, carbon offset programs, and electric delivery vehicles contribute to a greener Logistics and Distribution model. Ethical sourcing and labour practices also play a crucial role in building a responsible supply chain. Train and Empower Your Workforce Upskill Teams in Digital Tools and Analytics As technology continues to evolve, the need for a digitally skilled workforce becomes more urgent. Providing training in logistics software, data analytics, and emerging technologies equips employees to manage complex operations. Companies that invest in upskilling gain a competitive edge in Logistics and Distribution. Build Cross-Functional Teams Collaboration across departments is key to a cohesive Logistics and Distribution strategy. Cross-functional teams that include logistics, IT, customer service, and procurement professionals can solve problems faster and innovate more effectively. Encouraging collaboration leads to more efficient processes and better outcomes. Promote Leadership in Crisis Management Leaders play a critical role in navigating disruptions. Developing leadership skills in risk assessment, communication, and decision-making prepares teams to handle challenges confidently. Training programs focused on crisis management build resilience within Logistics and Distribution operations. Frequently Asked Questions Ending Notes The future of Logistics and Distribution in 2025 is defined by technology, agility, and customer focus. Businesses must embrace innovation, strengthen their networks, and empower their workforce to stay ahead. At KnoWerX, we specialise in preparing professionals for success through high-quality training and certification programs. With our guidance, you can master the strategies needed to dominate Logistics and Distribution and drive your career or business forward
Risk Analysis and Response: Overrated or Essential?

Risk Analysis and Response: Overrated or Essential? Imagine a multimillion-dollar project halted midway due to an unforeseen regulatory change. The team scrambles, budgets explode, and timelines collapse. The post-mortem reveals one glaring omission: the risk was never analysed, let alone planned for. In a world that’s becoming increasingly complex and uncertain, Risk Analysis and Response is no longer a luxury it may be the linchpin of sustainable decision-making. Yet, some argue it’s an overhyped, resource-draining exercise that rarely delivers on its promises. So, where does the truth lie? Let’s explore whether Risk Analysis and Response is genuinely essential or simply overrated. Understanding Risk Analysis and Response To understand the debate, it’s crucial to define the concept. Risk Analysis and Response refers to a structured approach used in project management and business planning to identify potential threats, assess their impact and likelihood, and implement appropriate strategies to mitigate or respond to them. This process typically involves: Risk Identification: Listing possible risks that might affect objectives. Risk Assessment: Evaluating the probability and impact of these risks. Risk Response Planning: Developing actions to avoid, reduce, transfer, or accept the risk. Monitoring and Control: Continuously tracking and managing risks as projects evolve. Tools like SWOT analysis, risk matrices, Monte Carlo simulations, and scenario planning often play vital roles in executing a successful Risk Analysis and Response strategy. Arguments for Its Essential Nature Improved Decision-Making One of the most compelling arguments in favour of Risk Analysis and Response is its role in enhancing decision-making. When you anticipate potential disruptions, you can prepare contingency plans, allocate resources efficiently, and reduce surprises. For instance, in construction projects, planning for material shortages or labour delays can prevent costly rework and penalties. In IT, risk analysis helps safeguard data and maintain business continuity during cyber-attacks. Minimises Financial Loss A comprehensive Risk Analysis and Response process helps organisations prevent or lessen the impact of risks that could lead to significant financial losses. This is especially critical in sectors like finance, energy, and manufacturing, where minor errors can lead to massive repercussions. A case in point: a global pharmaceutical company avoided a $50 million delay by identifying supply chain vulnerabilities early and rerouting production proactively. Mandatory for Compliance and Governance In many industries, regulatory bodies require evidence of formal risk management practices. Without robust Risk Analysis and Response, companies risk non-compliance, legal issues, and damage to reputation. Frameworks like ISO 31000 and PMBOK place heavy emphasis on risk management as a foundational requirement. Why Some Consider It Overrated Despite its apparent benefits, Risk Analysis and Response is not without criticism. Too Theoretical and Time-Consuming Many argue that traditional risk processes can be overly bureaucratic and consume disproportionate time and resources. Managers often feel like they’re “ticking boxes” rather than generating actionable insights. In fast-moving environments, the static nature of many risk models may also fail to keep pace. Inaccurate Predictions Critics also highlight the limitations of forecasting. Risk assessments rely heavily on assumptions, which are often flawed or based on incomplete information. The COVID-19 pandemic is a prime example a low-likelihood, high-impact event that was largely unaccounted for in most corporate risk plans. Misplaced Focus Sometimes, organisations over-prepare for minor, low-impact risks while overlooking more significant threats. This misplaced focus can drain energy and divert resources from more critical operational needs. Striking a Balance So, is Risk Analysis and Response essential or overrated? The answer may not be binary. The real value lies in how the process is applied. Make It Scalable Risk management doesn’t need to be complex to be effective. Tailoring the depth and breadth of Risk Analysis and Response to match the project size and nature ensures efficiency without sacrificing insight. For example, a startup may adopt a lightweight, agile framework, while a multinational corporation requires a more formal structure. Focus on Strategic Risks Rather than listing every conceivable threat, focus on those that directly affect key business objectives. Strategic alignment ensures that Risk Analysis and Response delivers meaningful input to top-level decisions. Integrate with Agile and Lean Models Modern organisations are increasingly blending risk management into agile methodologies. Risk backlogs, sprint-level risk reviews, and rapid response loops allow Risk Analysis and Response to remain dynamic and actionable. Leverage Technology Today’s digital tools from AI-based forecasting to cloud-based risk dashboards are making Risk Analysis and Response more data-driven and real-time. This transformation allows businesses to adapt to evolving threats without slowing down. Frequently Asked Questions Ending Notes At KnoWerX, we believe that Risk Analysis and Response is not just a theoretical concept it’s a strategic imperative in the world of Supply Chain Management. With global supply chains becoming more interconnected and vulnerable to disruptions, organisations must be proactive rather than reactive. Ignoring potential risks can lead to missed opportunities, financial loss, and operational breakdowns. As an institute dedicated to training professionals in supply chain excellence, KnoWerX equips learners with practical, industry-relevant knowledge on identifying, analysing, and responding to risks effectively. We empower supply chain leaders to build resilient systems, make data-informed decisions, and lead with confidence even in times of uncertainty. So, is Risk Analysis and Response overrated or essential? From a supply chain management perspective and from the lens of KnoWerX it is undeniably essential for building future-ready organisations that can thrive in a dynamic world. Image Reference: Freepik Disclaimer: All trademarks, logos, and brand names are the property of their respective owners. All company, product, and service names used in this website are for identification purposes only. Use of these names, trademarks, and brands does not imply endorsement.
How Global Supply Chain at Risk from Rising Tariffs

How Global Supply Chain at Risk from Rising Tariffs The introduction sets the stage by defining tariff hikes as increases in taxes imposed on imported or exported goods, which directly affect the Global Supply Chain. It highlights the critical role of the Global Supply Chain in enabling the seamless flow of goods, services, and raw materials across borders. Tariff hikes disrupt this interconnected network by raising costs and creating inefficiencies. This section provides a brief overview of how these disruptions ripple through industries, setting up the need to explore their mechanisms and solutions. II. Mechanisms of Disruption This section delves into how tariff hikes destabilize the Global Supply Chain through multiple channels: Increased Costs: Tariff hikes elevate the cost of importing raw materials and exporting finished goods, squeezing profit margins. For example, manufacturers reliant on the Global Supply Chain for components face higher production costs, which may be passed to consumers, affecting competitiveness. Supply Chain Bottlenecks: The Global Supply Chain experiences delays as customs processes become more complex due to tariff-related compliance. These bottlenecks disrupt logistics, causing inventory shortages or overstocking, which further strains the Global Supply Chain. Market Uncertainty: Tariff hikes introduce volatility in the Global Supply Chain by making demand and supply unpredictable. Businesses struggle with forecasting, leading to inefficiencies in production and distribution planning. Trade Relationship Strain: Retaliatory tariffs from trading partners exacerbate disruptions in the Global Supply Chain. This tit-for-tat escalation erodes trust, complicating long-term partnerships and trade agreements essential for a stable Global Supply Chain. III. Case Studies This section illustrates real-world impacts of tariff hikes on the Global Supply Chain through two examples: U.S.-China Trade War (2018-2020): Tariffs imposed during this period disrupted the Global Supply Chain for industries like electronics and agriculture. For instance, higher costs for imported components forced manufacturers to seek alternative suppliers, creating delays and inefficiencies in the Global Supply Chain. Recent Tariff Hikes in [Specific Region/Industry]: This placeholder for a current example (e.g., tariffs on steel in Europe) highlights ongoing challenges. It examines how specific sectors face supply shortages or cost spikes, underscoring the broader vulnerability of the Global Supply Chain to policy shifts. IV. Steps to Mitigate and Fix Disruptions This section outlines actionable solutions to address tariff-related disruptions in the Global Supply Chain: Short-Term Solutions: Businesses can diversify suppliers to reduce reliance on tariff-affected regions, ensuring continuity in the Global Supply Chain. Stockpiling critical inventory and renegotiating contracts to share cost burdens also help mitigate immediate impacts. Long-Term Strategies: Relocating manufacturing to regions with favorable trade policies strengthens the Global Supply Chain’s resilience. Investing in automation reduces dependency on imported goods, while advocating for stable trade agreements minimizes future disruptions. Collaboration and Policy Advocacy: Industry associations can collectively lobby for tariff reductions, supporting a smoother Global Supply Chain. Engaging policymakers ensures businesses’ concerns are addressed. Technology and Innovation: AI-driven analytics enhance visibility in the Global Supply Chain, enabling proactive adjustments. Blockchain ensures transparent trade documentation, reducing delays and costs. V. Economic and Social Impacts This section focuses on the broader consequences of tariff hikes beyond operational disruptions, examining their effects on economies and societies. Economic Consequences: Reduced Competitiveness of Affected Industries: Tariff hikes increase the cost of goods, making products from affected industries (e.g., manufacturing, agriculture) less competitive in global markets. For example, higher tariffs on imported steel can raise production costs for automakers, leading to higher prices and reduced market share. Potential Job Losses Due to Cost Pressures: As companies face squeezed margins from increased costs, they may cut jobs or halt expansion to remain profitable. For instance, small businesses reliant on imported goods may struggle to absorb tariff costs, leading to layoffs or closures. Social Implications: Increased Consumer Prices: Tariffs often result in higher prices for goods, as businesses pass on additional costs to consumers. This can lead to inflation, reducing purchasing power, particularly for low-income households. For example, tariffs on electronics could raise the cost of smartphones and laptops. Strain on Global Economic Equity: Tariff hikes can disproportionately affect developing nations reliant on exports, exacerbating economic inequality. For instance, tariffs on agricultural exports from poorer countries could limit their access to global markets, hindering economic growth. This section highlights the ripple effects of tariffs on economic stability and societal well-being, emphasizing the need for mitigation strategies. VI. Future Outlook and Preparedness This section explores the evolving landscape of global trade and how businesses and policymakers can prepare for ongoing and future tariff-related challenges. Emerging Trade Trends: Shift Towards Regional Trade Agreements: In response to tariff uncertainties, countries are increasingly forming regional trade blocs (e.g., RCEP, USMCA) to reduce reliance on global supply chains and stabilize trade. This trend could reshape supply chain strategies, encouraging businesses to prioritize regional suppliers. Rise of Protectionist Policies: Growing geopolitical tensions and economic nationalism are driving more countries to adopt protectionist measures, including tariffs. This creates a volatile trade environment, requiring companies to stay agile and monitor policy changes closely. Building Resilience: Strengthening Supply Chain Adaptability: Companies can invest in flexible supply chain models, such as dual-sourcing or modular production, to quickly pivot in response to tariff changes. For example, a manufacturer might maintain suppliers in multiple countries to avoid tariff-related disruptions. Investing in Workforce Training for Trade Compliance: As trade regulations become more complex, training employees in customs procedures, tariff classifications, and compliance can reduce delays and penalties. This is particularly critical for industries like pharmaceuticals, where regulatory adherence is stringent. This section underscores the importance of anticipating future trade dynamics and building proactive strategies to ensure supply chain resilience in a tariff-heavy world. These explanations provide a deeper understanding of how sections V and VI contribute to the outline, addressing the wider implications of tariff hikes and strategies for long-term preparedness. Ending Notes n an increasingly interconnected world, tariff hikes pose significant threats to the efficiency, stability, and resilience of the Global Supply Chain. As highlighted, these disruptions not only escalate costs and operational complexities but also carry deeper economic and social repercussions that can destabilise
These Types of Demand Are Driving Massive Profits!
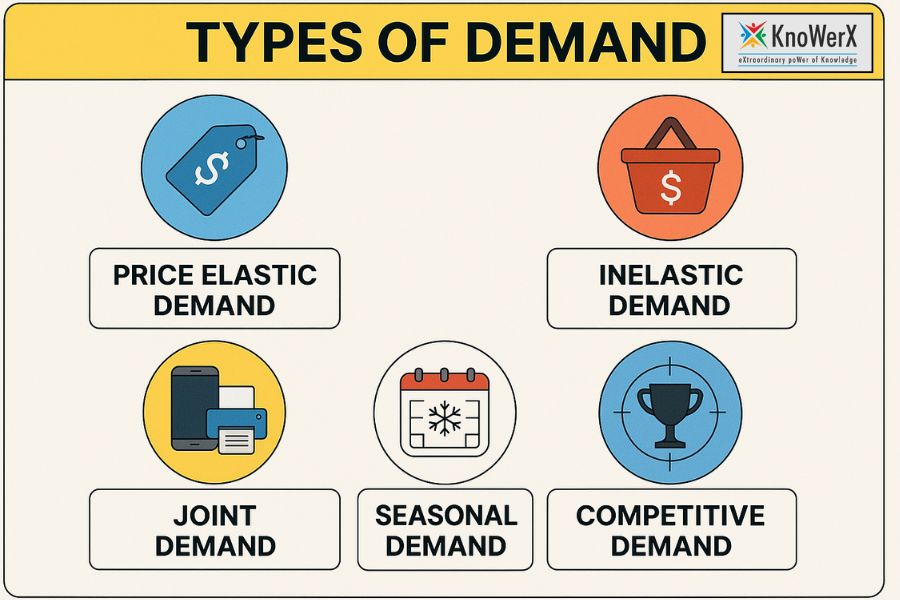
These Types of Demand Are Driving Massive Profits! Behind every successful business lies one powerful force demand. It’s the engine that drives sales, shapes strategy, and fuels profitability. But not all demand is created equal. From price-sensitive buyers to seasonal spikes and industry-driven needs, understanding the different types of demand is key to unlocking business growth. In this article, we’ll explore the most profitable demand types, reveal how businesses turn them into revenue streams, and show how supply chain professionals can use this knowledge to gain a competitive edge especially with guidance from KnoWerX, a leader in supply chain management education. 1. The Hidden Power of Demand Demand is the lifeblood of every business. Without demand, there is no reason to produce, no sales to make, and ultimately, no revenue to count. It is the unseen engine behind profits. There are various types of demand, each with its own influence on sales strategy. These include price elasticity, seasonality, and even competition-based demand — all crucial to how products perform in the market. Understanding and harnessing different types of demand can be a game-changer. Businesses that tailor their offerings and marketing based on dem and patterns often see faster growth, better customer retention, and higher margins. 2. Breaking Down the Most Profitable Types of Demand Here, we identify six highly impactful demand types and how businesses can strategically respond to each. 1 – Price Elastic Demand Consumers are highly sensitive to price changes in this type of demand. Lowering prices even slightly can lead to a significant increase in sales volume. Profit strategy: Leverage tactics like limited-time discounts, flash sales, and penetration pricing. These techniques attract price-sensitive customers, especially in competitive or commoditised markets. 2 – Inelastic Demand Here, consumers continue to buy regardless of price fluctuations. These are often necessities or products with few substitutes, like medicine or fuel. Profit strategy: Adopt premium pricing, especially for essential or high-value items. Margins can be maintained or increased without fearing a drop in demand. 3 – Derived Demand This demand exists because of the demand for another product or service. For example, the demand for steel arises from the demand for construction and automobiles. Profit strategy: Position your business within the B2B supply chain to benefit from upstream or downstream demand. Anticipate industry trends to align offerings with growth sectors. 4 – Joint Demand Products are often used together, so demand for one boosts the other. Printers and ink cartridges, or smartphones and protective cases, are classic examples. Profit strategy: Create product bundles or offer upsells that add value. This not only boosts average order value but also enhances customer satisfaction by delivering complete solutions. 5- Seasonal Demand Consumer interest surges during specific periods, such as holidays or weather changes. Think of ski gear in winter or air conditioners in summer. Profit strategy: Plan seasonal promotions well in advance and manage inventory smartly. Capitalising on high-demand windows can lead to a spike in revenues while minimising overstock risks. 6 – Competitive Demand Occurs when multiple products or brands satisfy the same need. For instance, Coke and Pepsi compete for the same consumer base. Profit strategy: Focus on brand differentiation, unique features, and emotional connections. Strong brand positioning can tip customer preference in your favour even in crowded markets. 3. How Businesses Turn Demand Types into Revenue Machines Successful businesses analyse consumer behaviour and evolving market trends. By doing so, they can match the right demand type to the right product or service strategy. Product development, pricing, and promotions must align with identified demand types. Whether through seasonal offerings or competitively priced innovations, aligning business decisions with demand can drive long-term revenue. Real-world case study: Consider how Starbucks uses seasonal demand (e.g., Pumpkin Spice Latte) and competitive demand (customisable coffee vs local cafés) to stay ahead. Their agile marketing and limited-time offers keep customers engaged year-round. 4. Adapting Your Business to Maximise Demand-Based Profits Invest in demand forecasting tools and advanced analytics to anticipate trends. Knowing when and how much customers will buy empowers smarter inventory, staffing, and pricing decisions. Marketing and sales efforts must be tailored to match the specific type of demand your product faces. For example, promotional campaigns should target price-sensitive consumers if your product faces elastic demand. Agility and innovation are key to surviving and thriving in demand-driven markets. Rapidly iterating on product features, bundles, or pricing models can help you capitalise on emerging demand types and outpace competitors. 5. The Role of Innovation in Shaping Demand Types Innovation doesn’t just respond to demand — it creates it. Companies that consistently innovate can shift consumer behaviour and even invent entirely new types of demand. Disruptive products often turn latent demand into mainstream markets. Think of how Netflix transformed the entertainment industry by responding to unmet desires for convenience and choice. Technology-driven businesses use R&D to unlock price-inelastic or joint demand. For example, smart homes combine hardware and software into bundles, enhancing long-term customer value. 6. Common Mistakes Businesses Make with Demand Strategy One-size-fits-all pricing often fails in markets with varying demand types. Businesses that ignore elasticity risk losing customers or underpricing high-demand products. Failing to align inventory with seasonal or derived demand leads to missed profits. Overstocking or stockouts can harm brand trust and create operational inefficiencies. Misreading competitive demand can weaken brand positioning. Brands that don’t differentiate may be viewed as interchangeable and get lost in price wars. Frequently Asked Questions Ending Remark At KnoWerX, we understand that recognising and responding to different types of demand is the cornerstone of any successful supply chain strategy. In today’s fast-paced and competitive market, businesses can no longer rely on one-size-fits-all approaches. They need professionals who can interpret demand patterns — whether price elasticity, seasonal surges, or derived and competitive demand — and translate them into actionable, profit-driving decisions. Our courses are designed to equip supply chain leaders with the tools and insights needed to forecast accurately, optimise inventory, and align operations with real market needs. Through frameworks, real-world case
Supply Chain Digitalization: Are You Falling Behind?

Supply Chain Digitalization: Are You Falling Behind? Supply chain digitalization refers to the adoption of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and blockchain to enhance supply chain operations. As global markets become increasingly interconnected, companies must embrace digital transformation to stay competitive. This shift enables businesses to improve efficiency, enhance visibility, and reduce operational costs. However, while many organizations are transitioning to digital supply chains, others are struggling with the challenges associated with implementation. Benefits of Supply Chain Digitalization Increased Efficiency and Automation: Digitalization streamlines supply chain processes by automating repetitive tasks such as order processing, inventory tracking, and logistics coordination. Automation reduces manual errors and speeds up operations, improving overall productivity. Real-Time Data Visibility and Decision-Making: Advanced digital tools provide real-time insights into supply chain performance. Companies can monitor inventory levels, track shipments, and predict demand fluctuations using data analytics. This enables faster and more informed decision-making, helping businesses avoid stockouts or overstocking. Cost Reduction and Improved Resource Allocation: By optimizing processes through digitalization, businesses can cut down on unnecessary costs related to logistics, warehousing, and procurement. Predictive analytics and AI-driven demand forecasting help allocate resources more efficiently, reducing waste and improving profitability. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction and Responsiveness: With real-time tracking and automated communication, customers experience better service and faster deliveries. Digitalization allows businesses to adapt quickly to market changes, ensuring that customer demands are met efficiently. Major Challenges of Supply Chain Digitalization High Implementation Costs: Implementing digital technologies requires substantial financial investment in software, hardware, and training. While large corporations may have the budget to adopt these solutions, small and mid-sized enterprises (SMEs) often struggle with the high initial costs. Integration with Legacy Systems: Many companies rely on outdated legacy systems that are not compatible with modern digital solutions. Upgrading or integrating these systems can be complex, time-consuming, and expensive. Without seamless integration, data inconsistencies can arise, reducing the effectiveness of digital transformation. Cybersecurity Risks: As Supply chain digitalization become more digitally connected, they become vulnerable to cyber threats such as data breaches, ransomware attacks, and hacking. Protecting sensitive supply chain data requires robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption, firewalls, and secure access controls. Workforce Skill Gap: A significant challenge in Supply chain digitalization is the lack of skilled professionals who can operate and manage digital tools. Many employees may resist change due to a lack of familiarity with new technologies, making it essential for businesses to invest in training and development programs. Data Management and Accuracy: Supply chain digitalization generate vast amounts of data, but ensuring its accuracy and reliability remains a challenge. Inconsistent or inaccurate data can lead to poor decision-making, inefficiencies, and supply chain disruptions. Companies must implement data governance policies and advanced analytics tools to maintain data integrity. Supplier and Partner Collaboration: For digital transformation to be successful, all stakeholders in the supply chain digitalization, including suppliers, logistics partners, and manufacturers, must be on board. However, not all suppliers may be willing or capable of adopting digital technologies, leading to inconsistencies in data sharing and operational efficiency. Businesses must work closely with their partners to align digital strategies and ensure smooth collaboration. Strategies to Overcome These Challenges Investing in Scalable Digital Solutions: Businesses should adopt scalable and flexible digital technologies that can grow with their needs. Cloud-based solutions, modular ERP systems, and AI-driven analytics can help organizations transition to digital supply chains more efficiently. Strengthening Cybersecurity Frameworks: To protect digital supply chains from cyber threats, companies must invest in robust cybersecurity measures, including data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring of network security. Providing Continuous Training for Employees: Workforce training and upskilling are critical to overcoming the digital skill gap. Businesses should implement ongoing learning programs to ensure employees are equipped with the necessary digital skills. Encouraging a culture of continuous learning and innovation can further enhance adaptability in an evolving digital landscape. Developing a Phased Digital Transformation Roadmap: Instead of attempting a complete digital transformation at once, businesses can adopt a phased approach. By gradually implementing digital solutions in specific areas, companies can minimize risks, control costs, and ensure a smoother transition. Ending Remark Supply chain digitalization is no longer an option but a necessity for businesses aiming to remain competitive in today’s fast-paced global market. While challenges such as high implementation costs, cybersecurity risks, and workforce skill gaps exist, companies that proactively address these obstacles can unlock significant efficiency and profitability gains. At KnoWerX – an Institute of Supply Chain Management, we understand the complexities of digital transformation in supply chains. Our specialized training programs equip professionals with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate digitalization effectively. From mastering advanced analytics to understanding automation and cybersecurity in supply chains, KnoWerX ensures that supply chain professionals are well-prepared for the future. By investing in the right education and strategies, businesses can overcome digitalization challenges and build a more agile, data-driven, and resilient supply chain. Image Reference: Freepik Disclaimer: All trademarks, logos, and brand names are the property of their respective owners. All company, product, and service names used in this website are for identification purposes only. Use of these names, trademarks, and brands does not imply endorsement.
